IoT in Retail Industry – Use Cases, Benefits and Applications
A quiet revolution is occurring in the busy world of contemporary retail, fueled by the easy incorporation of technology into every facet of the buying experience. With its network of linked devices and sensors, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a disruptive force that is changing how merchants run their businesses, interact with their customers, and streamline their operations.
Imagine entering a smart retail establishment where every move you make, the item you select, and the aisle you pursue are painstakingly monitored and evaluated. Real-time inventory level detection on smart shelves allows them to recommend restocks before they run out of goods.
Digital signage dynamically creates personalized shopping experiences by modifying promotions according to customers’ demographics and preferences. With its ability to improve efficiency and customer happiness simultaneously, this networked ecosystem of gadgets is more than just a futuristic concept; it is the Internet of Things revolution in action.
IoT technologies are having a more noticeable effect on retail as they develop. Consider a store that sells apparel and uses RFID tags sewn into the clothing. Sensors recognise this interaction when a customer tries on an item of apparel and update the inventory system automatically.
Data analytics algorithms process this information concurrently and offer insights into fitting trends, popular styles, and inventory turnover rates. Retailers are able to make well-informed decisions by using this real-time data, which helps them with anything from dynamic pricing strategies to product placement optimisation.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is about more than just connecting things; it’s about using data wisely to propel corporate expansion and provide unmatched customer experiences. This article explores the many dimensions of the Internet of Things retail revolution and its significant effects on customers and industry players.
What is Retail, and what role does it play in IoT?
Selling products or services to customers via a variety of channels, including physical storefronts, internet platforms, or a combination of both, is referred to as retail. It includes a broad spectrum of businesses, ranging from groceries and household goods to electronics and fashion. Acting as a liaison between suppliers and final customers, the retail industry is vital to the economy. It includes everything from tiny neighbourhood stores to massive international chains, all of which enhance the general shopping experience and boost customer happiness.
Retail experienced a significant metamorphosis within the Internet of Things. IoT technology creates a network of smart systems that gather, process, and share data in real-time by integrating hardware, software, sensors, and networking. Because of its ability to improve consumer experiences, increase productivity, and facilitate data-driven decision-making, connectivity is revolutionizing retail operations.
Inventory management is a major area where IoT is used in retail. Thanks to RFID tags and IoT-enabled devices, retailers have real-time visibility into their stock levels. This data accuracy streamlines supply chain logistics decreases overstocking and avoids stockouts. By automating inventory tracking and replenishment procedures, retailers may optimize their stocking levels, cut expenses, and boost overall operational efficiency.
IoT also improves the retail consumer experience. Thanks to connected technologies like smartphone apps, interactive displays, and smart mirrors, shopping experiences can be customized. RFID-enabled smart mirrors provide one example of a customized and smooth shopping experience, which can recommend complementary items based on what customers try on. IoT-integrated mobile apps can encourage user engagement and loyalty by sending tailored promotions, recommendations, and loyalty benefits.
Moreover, IoT-driven analytics give merchants important knowledge about the preferences, trends, and behaviour of their customers. Retailers can gain a deeper understanding of their consumers’ needs and preferences by analyzing data from social media interactions, linked device data, and purchase histories. Targeted marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and pricing strategies are made possible by this data-driven strategy, which eventually increases sales and improves consumer happiness.
All things considered, IoT transforms retail by streamlining processes, improving consumer experiences, and opening up fresh doors for expansion and creativity in the sector.
The Rise of IoT in Retail
IoT’s emergence in retail has, in fact, completely changed the industry. Smart sensors are essential because they give retailers access to real-time inventory level data, which helps them manage inventory more efficiently and cut expenses. RFID tags make it possible to trace products effectively along the supply chain, which enhances visibility and streamlines logistical processes. By providing customers’ smartphones with personalized marketing and navigation support, beacons improve the in-store experience.
Additionally, thanks to connected equipment like checkout systems and smart shelves, businesses can obtain important information about their customer’s behaviour and preferences. Retailers may improve consumer satisfaction and loyalty by customizing marketing campaigns, optimizing shop layouts, and providing personalized recommendations through the use of IoT data analytics.
IoT technology also powers innovations like autonomous drone deliveries, cashierless checkout systems, and smart vending machines, which are all outside the typical brick-and-mortar business. These developments improve the entire shopping experience, generate new revenue sources, and increase operational efficiency.
All things considered, IoT integration in retail is revolutionizing the sector and opening the door to smarter, more connected, and customer-focused retail spaces.
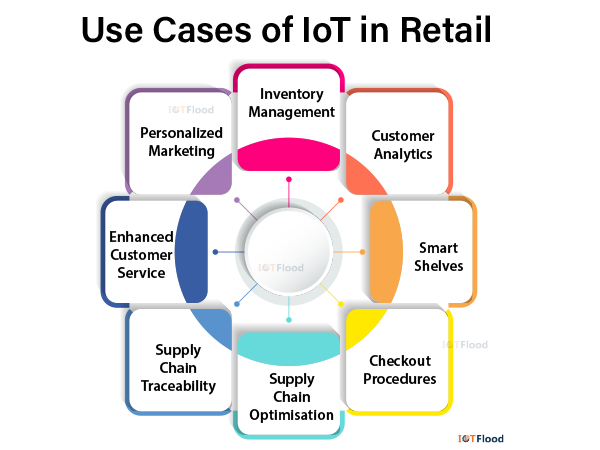
Use Cases of IoT in Retail
IoT is applied in retail in a number of ways to boost productivity, improve consumer satisfaction, and spur company expansion. The following are some significant IoT uses in retail:
Inventory management: By using IoT sensors and RFID tags to track inventory in real-time, retailers can precisely monitor stock levels, minimize out-of-stock situations, and expedite inventory replenishment procedures.
Supply Chain Optimisation: By giving retailers visibility into every step of the supply chain, from the warehouse to the shop shelves, IoT devices enable them to improve logistics, cut down on transportation expenses, and guarantee on-time delivery.
Smart Shelves: IoT-enabled smart shelves automatically monitor product levels and may also send out warnings when replenishment is necessary. This technology lessens the need for manual labor, increases shelf availability, and improves the entire shopping experience.
Personalized Marketing: Retailers can use beacons and Internet of Things (IoT)- connected devices to offer customers personalized discounts, promotions, and suggestions based on their location, preferences, and past purchases.
Customer analytics: IoT data analytics technologies gather and examine information on consumer behavior, including dwell periods, foot traffic patterns, and product interactions. Retailers utilize this data to enhance marketing campaigns, optimize store layouts, and comprehend consumer preferences.
Checkout Procedures: Self-checkout kiosks and cashier-less checkout options are examples of IoT-based checkout systems that improve operational efficiency, expedite payments, and shorten lines.
Loss Prevention: IoT technologies enable shops to stop inventory shrinkage, identify theft instances in real-time, and enhance security measures. Examples of these technologies include smart surveillance cameras and RFID-based anti-theft devices.
Supply Chain Traceability: End-to-end product traceability is made possible by IoT-powered sensors and blockchain technology, which enables retailers and customers to confirm the provenance, route, and validity of items, especially in sectors like food and medicine.
Enhanced Customer Service: By offering customers self-service alternatives, product information, and tailored recommendations, Internet of Things (IoT) devices—like interactive kiosks and digital signage—improve the whole shopping experience.
Predictive Maintenance: By integrating IoT sensors into equipment and store architecture, merchants can proactively identify and address possible faults before they cause operational disruptions.
All things considered, IoT in retail transforms how companies run, interact with clients, and maximize many facets of their operations, resulting in increased productivity, profitability, and client happiness.
Benefits of IoT in Retail
The retail industry has experienced a revolutionary shift in how firms function and interact with customers due to the Internet of Things (IoT). The Internet of Things (IoT) provides a host of advantages that improve productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance in retail environments by combining smart sensors, linked devices, and data analytics.
Here are a few advantages of IoT in retail:
Real-Time Inventory Management: Retailers may optimize stock levels, lower stockouts, and increase inventory turnover by using real-time data on inventory levels via IoT sensors and RFID tags.
Enhanced consumer Experience: IoT-powered personalized suggestions, targeted promotions, and interactive in-store experiences increase consumer engagement, contentment, and loyalty.
Operational Efficiency: IoT solutions reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and improve overall operational efficiency by automating tasks like inventory tracking, restocking, and checkout.
Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing insightful information about consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing trends, IoT analytics help retailers make data-driven choices, enhance their product offerings, and optimize their pricing plans.
Supply Chain Optimisation: IoT-enabled supply chain visibility, predictive maintenance, and logistics optimisation boost overall supply chain efficiency by lowering costs, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring on-time delivery.
Better Loss Prevention and Security: Internet of Things (IoT)-based surveillance systems, anti-theft gadgets, and access control solutions protect sensitive data and physical assets by lowering shrinkage, reducing risks, and enhancing shop security.
Sustainability and Cost Savings: Internet of Things (IoT) technology assists retailers in reducing energy use, waste, and resource optimization, which improves sustainability practices, lowers costs, and has a beneficial environmental impact.
Omnichannel Integration: The Internet of Things makes it easier for online and offline channels to integrate seamlessly, giving merchants the ability to provide customers with a unified shopping experience, individualized services, and consistent brand messaging across all touchpoints.
Flexibility and Scalability: IoT solutions are flexible and scalable to changing business requirements, enabling retailers to grow their businesses, launch new services, and develop cutting-edge goods while remaining agile and flexible in a constantly changing market.
Competitive Advantage: Using IoT in retail gives businesses an edge over rivals thanks to personalized experiences, inventive services, effective operations, and data-driven marketing tactics that set them apart from the competition and help them draw in and keep consumers in a cutthroat market.
All things considered, IoT in retail provides a plethora of advantages that spur company expansion, raise customer satisfaction, streamline processes, and open doors for creativity and uniqueness in the retail sector.
Use Cases
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is driving a major revolution in the retail sector. The Internet of Things (IoT) has completely changed how merchants handle their inventories, improve consumer satisfaction, and streamline supply chain processes. Retailers may take advantage of the Internet of Things (IoT) to increase operational efficiency, boost customer engagement, and obtain a competitive edge in the market by utilizing smart sensors, RFID tags, beacons, and data analytics.
In light of this, let’s examine several significant Internet of Things use cases in the retail industry, emphasizing how these innovations are changing supply chain operations, improving consumer experiences, and changing inventory management.
1. Inventory Management: Inventory management is the process of monitoring, regulating, and streamlining the movement of supplies and products inside an organization. It entails keeping track of the items, components, raw materials and completed items that a business has on hand. Effective inventory management ensures that the correct products are available in the right quantities, at the right times, and in the right locations to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing profitability.
Real-time inventory tracking: Retailers may precisely track inventory levels in real-time by placing RFID tags and IoT sensors on products, shelves, and storage facilities. This information is essential for reducing overstocking, averting stockouts, and increasing inventory turnover.
Automated Replenishment: Through system integration with suppliers, Internet of Things (IoT) solutions automate inventory replenishment procedures. IoT platforms immediately initiate purchase orders or reorder requests when stock levels exceed predetermined criteria, guaranteeing effective product restocking.
Shelf Monitoring: IoT-enabled smart shelves monitor product rotation, positioning, and expiration dates. They can recognise low inventory levels, notify personnel or automated systems when restocking is necessary, and maximize shelf space for better product display.
2. Customer Experience Enhancement: The term “customer experience enhancement” describes the methods, procedures, and tools that companies use to enhance and customize client encounters and satisfaction levels all across the customer journey. It entails each and every point of contact and engagement a consumer has with a company, good, or service, with the goal of delivering seamless, enjoyable experiences that either meet or surpass their expectations.
Personalized Suggestions: Internet of Things (IoT) analytics examine client data, such as surfing habits, past purchases, and demographic data. Using this data, personalized product recommendations, promotions, and offers that cater to the interests and tastes of individual customers are created.
In-store Navigation: Customers can receive in-store navigation support with beacon technology and smartphone apps connected to the Internet of Things. These systems can direct customers to particular departments, items, or promotions based on where they are in the store, which increases convenience and elevates the whole shopping experience.
Interactive Displays: IoT-enabled interactive displays—like digital signage, kiosks, and AR/VR experiences—engage customers by using dynamic content, product details, reviews, and virtual try-on experiences. These interactive features draw users in, lengthen their stays, and influence purchases.
3. Supply Chain Optimization: Supply chain optimization is the strategic process of refining and streamlining the several elements, actions, and procedures that make up the supply chain to increase productivity, reduce expenses, improve flexibility, and successfully satisfy consumer demand. It entails streamlining the movement of products, data, and money along the whole supply chain network, from suppliers to manufacturers to distributors to retailers to customers at the end.
Real-time tracking: Throughout the supply chain, sensors and GPS trackers are used by IoT devices to monitor cars, shipments, and items in transit. Thanks to this real-time information, retailers can keep an eye on delivery status, optimize routing, and react quickly to delays or interruptions.
Predictive Maintenance: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors positioned on machines, appliances, and cars gather information on usage trends, wear and tear, and performance indicators. This data is analyzed by predictive analytics algorithms to forecast maintenance requirements, plan preventive maintenance activities, reduce downtime, and increase asset longevity.
Collaboration with Suppliers: IoT platforms share real-time data on demand projections, inventory levels, production plans, and delivery dates, facilitating smooth collaboration with suppliers. Through this partnership, the supply chain becomes more visible, coordination improves, lead times are shortened, and the proper supplies are always available.
Potential Cost Savings of Using IoT in Retail
The Internet of Things (IoT) can save a lot of money in retail in a number of ways. The following are some possible cost-saving advantages of IoT use in retail:
Supply Chain Optimisation: The Internet of Things (IoT) allows you to follow items in real time along the whole supply chain, lowering transportation costs, reducing delays, and boosting overall effectiveness.
Customer insights: IoT devices like cameras and beacons can obtain information on consumer behavior, preferences, and traffic patterns. Analyzing this data can result in better marketing plans, more focused promotions, and enhanced customer experiences, which will ultimately increase sales and cut marketing expenses.
Checkout Automation: By eliminating the need for manned checkout counters, IoT-powered self-checkout systems can save labor costs.
Prevents Theft and Fraud: By preventing theft and fraud, IoT solutions such as smart locks and security cameras can help lower losses related to shrinkage.
Inventory management: IoT devices like sensors and RFID tags make real-time inventory tracking easier for shops. This optimizes inventory levels and lowers holding costs by reducing the chance of overstocking or stockouts.
Predictive Maintenance: By identifying problems early on, IoT-enabled gadgets such as sensors in retail equipment (lighting, cooling systems, etc.) enable proactive maintenance. By doing this, expensive equipment downtime and repair expenditures can be avoided.
Energy Efficiency: Smart HVAC and lighting systems that adapt to occupancy and ambient circumstances can reduce energy expenditures over time. IoT sensors can also pinpoint locations for optimal energy use.
Optimized Store Layout: IoT data analytics can provide businesses with information on the best product placements and store layouts, improving the shopping experience and possibly raising sales per square foot.
Remote Monitoring: The Internet of Things (IoT) makes it possible to remotely monitor several shop locations from a single dashboard, eliminating the need for workers to be present on-site at all times and possibly saving management money on travel expenses.
All things considered, utilizing IoT in retail can save money by increasing operational effectiveness, improving customer experiences, cutting waste, and facilitating better decision-making based on real-time data insights.
How can IoT help retailers reduce labor costs?
Retailers can lower labor expenses in a number of ways with IoT:
Task Automation: Temperature monitoring, lighting control, and security checks are just a few of the repetitive jobs that Internet of Things devices can automate. Employees can concentrate on more strategic work because of the automation that cuts down on the amount of time they spend on manual operations.
Checkout Automation: By eliminating the need for manned checkout counters, IoT-powered self-checkout systems can minimize labor expenses related to checkout procedures and result in fewer cashier shifts.
Optimised Staff Scheduling: Retailers can optimize staff scheduling by using insights from IoT data analytics into customer traffic patterns and peak hours. This keeps the proper amount of workers on hand during peak hours and prevents overstaffing during off-peak hours.
Automated Inventory Management: IoT sensors can monitor inventory levels in real-time, eliminating the need for manual stock inspections and counts. Because of this automation, staff have more time to devote to higher-value jobs.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors and in-store equipment make proactive maintenance possible, allowing for early problem identification. This lowers labor costs related to maintenance and repairs by minimizing equipment downtime and the need for reactive repairs.
Remote Management and Monitoring: The Internet of Things makes it possible to monitor equipment and store operations remotely. Supervisors can spot problems, make changes, and even troubleshoot from a distance, eliminating the constant need for on-site workers.
Enhanced Productivity and Training: Based on performance data gathered from sensors and devices, IoT can enable customized training programmes for staff members. By increasing worker productivity and effectiveness, this focused training can lessen the need for hiring more personnel.
Optimized Store Layout: By using data analytics from IoT devices, merchants may locate products and arrange their stores more strategically in response to consumer preferences and behavior. A well-planned store layout can boost customer satisfaction, cut down on staff time spent replenishing shelves, and increase operational effectiveness.
By strategically utilizing IoT solutions, retailers may maintain or even increase customer service levels while streamlining operations, increasing productivity, and lowering labor costs.
What are the examples of IoT devices in Retail?
There are several instances of IoT devices being employed in a variety of retail applications. Here are a few typical instances:
RFID Tags: Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags are used for inventory management and tracking. Retailers may attach them to products, pallets, or containers to follow the flow of items through the supply chain and in-store. They allow merchants to monitor product movement across the supply chain and in-store.
Smart Shelves: Smart shelves use sensors to identify when products are added or removed, providing real-time inventory information. They can also use digital displays to show prices, promotions, and product details.
Beacons: Beacons are tiny, Bluetooth-capable gadgets positioned throughout stores to connect with patrons’ smartphones. They can send personalized offers, incentives, and notifications according to the customer’s location and preferences.
IoT Cameras: IoT-enabled cameras are used for security, customer analytics, and operational monitoring. They can monitor consumer flow, identify questionable activity, and offer performance data for individual stores.
Self-Checkout Kiosks: Using Internet of Things technology, self-checkout kiosks let customers scan and pay for their goods without help from a cashier. These payment kiosks expedite the checkout process and accept a variety of payment options.
Smart Mirrors: IoT-enabled smart mirrors are utilized in changing rooms. They can improve the shopping experience by displaying product details, suggesting related products, and offering virtual try-on experiences.
Temperature and Humidity Sensors: These sensors monitor conditions in store areas, such as the refrigerated sections for perishable items, where temperature and humidity management are crucial.
Smart Lighting Systems: Internet of Things-enabled lighting systems that change color and brightness according to occupancy, daylighting conditions, and natural light levels. They can also be employed in marketing, for example, to draw attention to special offers or set the mood.
Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs): These are remotely updateable digital pricing tags. They enable retailers to use dynamic pricing methods and eliminate the necessity for manual price adjustments.
Mobile Point-of-Sale (mPOS) Devices: The IoT-enabled handheld gadgets enable employees to handle transactions from any location within the store. They can also give clients individualized product recommendations, inventory availability, and details about the products.
These examples show how IoT devices are being utilized in retail to boost consumer experiences, increase operational efficiency, and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
Internet of Things in Retail: Market Trends
The revolutionary possibilities of the Internet of Things (IoT) are altering the retail industry and resulting in several noteworthy market trends. One noteworthy trend is the emphasis on customized customer experiences. Thanks to IoT devices, retailers may collect real-time data on consumer behavior, preferences, and purchase habits. By utilizing this data, retailers can offer individualized specials, design marketing campaigns, and make product recommendations based on the tastes of certain customers. This customized strategy encourages repeat business and customer loyalty in addition to improving client pleasure.
A notable development in retail enabled by IoT is the smooth amalgamation of omni-channel experiences. The Internet of Things (IoT) allows retailers to offer a consistent purchasing experience across different touchpoints by bridging the gap between online and offline channels. Regardless of the channel consumers select, click-and-collect, in-store pickups and synchronized inventory management are just a few of the features that guarantee seamless client interaction with the brand. This integration maximizes operational efficiency for shops while also improving client convenience.
The use of IoT in retail has also significantly increased supply chain efficiency and visibility. Real-time insights into inventory levels, shipment status, and logistical operations are available through Internet of Things devices, including RFID tags, sensors, and GPS trackers. Thanks to this increased visibility, retailers can make data-driven decisions, optimize inventory management, lower stockouts, and increase overall supply chain efficiency. Thus, with dependable and effective supply chain operations, businesses may increase customer happiness, deliver goods more quickly, and save expenses.
Furthermore, traditional retail locations have undergone a revolution thanks to IoT-driven smart store solutions. Thanks to interactive displays, digital signs, beacons, and smart shelving, customers can experience immersive and interesting settings. These innovations improve customer interaction, product discovery, and in-store navigation, which boosts revenue and elevates brand perception.
Furthermore, a safe shopping environment is guaranteed by IoT-powered security and loss prevention solutions, which also safeguard assets and lower shrinkage.
All things considered, IoT in retail is fostering innovation, competitiveness, and customer-centricity, which improves the experience for both customers and retailers.
Successful Retail IoT Applications
1. Foot Traffic Monitoring:
- Objective: To enhance customer experience and operational efficiency by analysing and optimising customer movement and store layouts.
- Implementation: Tracks consumer movement and dwell periods in various retail locations using sensors or video-based surveillance.
- Benefits: It allows for data-driven store layout alterations, which improve sales and customer happiness, as well as real-time customer help and personalised shopping experiences.
2. Predictive Equipment Maintenance:
- Objective: To minimise downtime, optimise energy use, and anticipate equipment problems.
- Implementation: Sensors are used to monitor performance indicators such as temperature, pressure, and energy consumption in equipment such as HVAC systems and refrigeration units.
- Benefits: Ensures food safety compliance in retail contexts, enables proactive maintenance, and reduces costs through energy efficiency.
3. Demand Alert Warehouses:
- Objective: Automate warehouse processes by using demand trends and real-time sales data.
- Implementation: Tracks inventory levels, forecasts demand, and improves warehouse processes with the use of IoT sensors, RFID technology, and data analytics.
- Benefits: It increases order fulfilment speed, decreases stockouts, improves inventory management accuracy, and increases overall supply chain efficiency.
4. Smart Fulfilment:
- Objective: To improve transportation, tracking, and delivery systems in order to move items more quickly and efficiently.
- Implementation: It uses route optimization algorithms, RFID tags, GPS trackers, and other Internet of Things devices to monitor and control the movement of items.
- Benefits: minimising delivery errors, improving customer happiness, optimising delivery routes to cut costs and time, and providing real-time visibility into shipment whereabouts.
All things considered, these IoT applications for retail help build smarter, more integrated, and more effective retail ecosystems, which eventually improve customer satisfaction, boost productivity, and improve business outcomes.
Real-World Examples
Real-world IoT examples in retail demonstrate the technology’s practical applications and benefits. Here are a few noteworthy instances:
Amazon Go Stores: One of the best examples of IoT in retail is Amazon’s cashier-less locations. These retailers follow their customers’ movements and automatically charge them for the things they pick up using a network of cameras, sensors, and machine learning algorithms. IoT technology makes this smooth checkout process feasible, resulting in a frictionless retail environment.
Zara’s RFID-enabled Stores: The international fashion retailer has integrated RFID technology to track inventories in real time throughout its stores. By attaching RFID tags to clothing items, stock inconsistencies can be decreased, automatic inventory counts may be made, and overall inventory accuracy can be increased. With the use of this IoT technology, Zara is able to improve customer shopping experiences and optimize stock levels.
Walmart’s IoT-enabled Supply Chain: To improve its supply chain processes, Walmart uses IoT devices, including temperature monitors, GPS trackers, and sensors. These devices provide real-time information on product location, shipment status, and weather conditions. Walmart uses this data to enhance supply chain effectiveness, guarantee product quality, and optimize logistics.
Nike’s Smart Store Concept: To improve consumer experiences, Nike has unveiled smart store designs that make use of IoT technologies. Nike’s flagship stores, for example, have interactive displays, digital signage, and smartphone apps that offer individualized in-store experiences, fitness tracking, and product recommendations.
Kroger’s Edge Shelf System: Leading supermarket giant Kroger has installed Edge Shelf systems driven by IoT at a few of its locations. These smart shelves provide real-time pricing, promotions, and product details via sensors and digital displays. Additionally, the technology collects information on consumer interactions, which aids Kroger in improving customer engagement and making data-driven decisions.
Starbucks’ Mobile Order & Pay: This system, which lets users order and pay for drinks via a smartphone app, uses Internet of Things technologies. Through communication with Internet of Things-enabled coffee makers, the app alerts baristas to incoming orders and expedites the preparation process. This IoT system increases consumer convenience, decreases wait times, and improves order accuracy.
Target’s Smart Lighting System: Target has used Internet of Things (IoT)-based intelligent lighting solutions in its retail locations to enhance energy efficiency and personalize the shopping experience. These systems modify lighting levels in response to occupancy, daylighting, and natural light levels. Target also employs beacon technology to deliver messages and promotions to customers’ smartphones based on their location.
These real-world examples highlight the wide range of IoT applications in retail, from automated checkout systems and inventory management to personalized customer experiences and energy-efficient operations. These examples demonstrate how IoT technology is transforming the retail sector and spurring creativity in a range of retail markets.
Challenges and Solution
Retailers must find strategic solutions to overcome the obstacles posed by navigating the IoT retail revolution. One of the biggest issues is handling worries about data security and privacy. IoT devices are gathering enormous volumes of consumer data, so protecting data privacy and putting strong cybersecurity safeguards in place is critical. To earn customers’ trust and secure sensitive data, retailers must place a high priority on data protection, encryption, access control, and compliance with data privacy laws like the CCPA and GDPR.
Another issue retailers face is interoperability across IoT devices. As the IoT ecosystem expands, it becomes more difficult to ensure that devices from different manufacturers are compatible and communicate seamlessly. Device interoperability standards and protocols, such as MQTT, CoAP, and OPC UA, are crucial for integrating IoT solutions efficiently and preventing siloed systems that impede analytics and data sharing.
Handling the massive amount of data produced by Internet of Things devices poses a challenge to analytics and scalability. To extract useful insights from IoT data, retailers need to make investments in machine learning algorithms, cloud infrastructure, and strong data analytics platforms. With the use of advanced analytics tools like sentiment analysis, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics, retailers may enhance decision-making based on real-time data insights, optimize operations, and personalize marketing campaigns.
Notwithstanding these difficulties, there are many opportunities for cooperation, innovation, and partnership in the IoT retail space. Cooperative efforts among industry stakeholders, such as retailers, technology providers, regulators, and cybersecurity specialists, can facilitate the establishment of industry standards and best practices for IoT security, interoperability, and data governance.
Additionally, utilizing cutting-edge technology like blockchain to improve data security and transparency offers chances to improve accountability and trust in IoT ecosystems. In order to address issues with data integrity, authentication, and provenance, blockchain-based solutions can provide safe data exchange, unchangeable audit trails, and transparent transactions.
Ultimately, adopting collaboration, innovation, and technology-driven solutions can unlock enormous value, drive competitive advantage, and deliver exceptional customer experiences in the IoT-powered retail landscape—all while navigating the challenges posed by the retail revolution requires careful planning and investment.
Future Prospects
IoT applications in retail have a bright future ahead of them and are anticipated to keep developing in a number of important sectors, including:
Enhanced Customer Experience: IoT technologies enable retailers to better understand consumer preferences and behaviour patterns, as well as to optimise inventory based on demand projections, by personalising shopping experiences through data analytics.
Supply Chain Optimisation: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors can monitor product conditions (e.g., temperature or humidity for perishable items) throughout transit, track inventory levels, and optimise logistics for effective inventory management.
In-Store Operations: Smart shelves, beacons, and RFID tags can enhance in-store operations by automating inventory tracking, enabling customised promotions, and improving the shopping experience.
Checkout Processes: Self-checkout kiosks and mobile payment options are examples of IoT-enabled checkout systems that shorten wait times and increase consumer convenience.
Safety and Security: Smart alarms, access control systems, and surveillance cameras are examples of IoT devices that improve store security by instantly identifying and addressing possible threats.
Data analytics and AI: By combining IoT-generated data with AI and machine learning algorithms, retailers can gain practical insights into anticipating customer patterns, refining pricing strategies, and enhancing marketing campaigns.
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Retail IoT applications are anticipated to combine with other emerging technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), to offer immersive shopping experiences, virtual try-on solutions, and interactive product demos.
However, to fully realise the potential of IoT in retail, issues, including cybersecurity risks, data privacy concerns, and the requirement for compatibility among various IoT devices and platforms, must be resolved. All things considered, retail IoT applications have a bright future ahead of them, with more innovation and acceptance predicted to bring about major advantages for both consumers and merchants.
Conclusion
To sum up, the revolution in IoT retail signifies a substantial paradigm shift that goes beyond simple technological progress. It transforms the way retailers engage with their clientele, streamlines operations, and introduces novel business strategies. Retailers can build seamless, personalized experiences that appeal to today’s digitally empowered consumers by integrating IoT technologies. IoT also gives shops the ability to lower expenses, simplify processes, and look for novel ways to generate income, which promotes competitiveness and long-term growth.
Retailers need to take the initiative when it comes to innovation and digital transformation going forward. This entails making investments in scalable Internet of Things solutions that complement their corporate goals, making sure that data privacy and security protocols are strong, and encouraging an environment that is always learning and adapting. In order to fulfil the constantly shifting demands of contemporary consumers, stay relevant in a competitive market, and navigate the rapidly changing IoT landscape, it will be imperative to embrace agility and flexibility.
In the end, those who fully embrace the IoT retail future stand to gain a great deal. By strategically utilizing IoT technologies, retailers can not only prosper in the current digital era but also help shape the industry’s future by offering unmatched consumer experiences, promoting operational excellence, and opening up new growth and innovation opportunities.