The Role of IoT in Supply Chain Optimization
The supply chain is a competitive advantage for companies looking to thrive in today’s fast-paced industries, as well as a logistical need. The requirement for effective supply chain management is more significant than ever as global markets become more integrated and customer needs change.
The Internet of Things (IoT) provides a suite of technologies that enable the transformation of conventional supply chains into flexible, data-driven ecosystems. By utilizing IoT devices, sensors, and data analytics, organizations may obtain unmatched visibility, control, and insights into every facet of their supply chain operations. The effects of IoT on supply chain optimization are complex.
IoT helps businesses to increase customer happiness, cut costs, optimize operations, and spur innovation with features like predictive maintenance for machinery and real-time tracking of commodities in transit. Businesses may proactively handle supply chain issues, including inventory control, demand forecasting, compliance, and sustainability, by leveraging the potential of IoT.
The potential advantages of IoT adoption significantly outweigh its difficulties, notwithstanding certain obstacles, including data security, interoperability, and skill shortages. With IoT continuing to develop and combine with other cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence, supply chain optimization has a bright future for businesses ready to embrace digital transformation. This article explores IoT’s applications, advantages, difficulties, and potential in supply chain optimization.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Definition:
Supply chain management, or SCM, is a strategic approach to managing the interrelated activities, processes, and resources involved in the sourcing, procurement, production, logistics, and distribution of goods and services. It seeks to maximize the movement of goods, data, and funds from suppliers to final consumers along the whole supply chain network. SCM includes planning, coordinating, collaborating, and working towards continuous improvement to increase productivity, lower expenses, lessen risks, and successfully satisfy customer demands.
Look at a multinational electronics manufacturer of cell phones, for instance. Supply chain management entails arranging with vendors worldwide to acquire raw materials such as metals, polymers, and electronic components. The business then produces cell phones, monitors stock levels, and works with logistics partners to ensure prompt delivery to retailers or clients. Demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and supply chain visibility are examples of SCM tactics essential to guarantee prompt delivery, economy, and client delight.
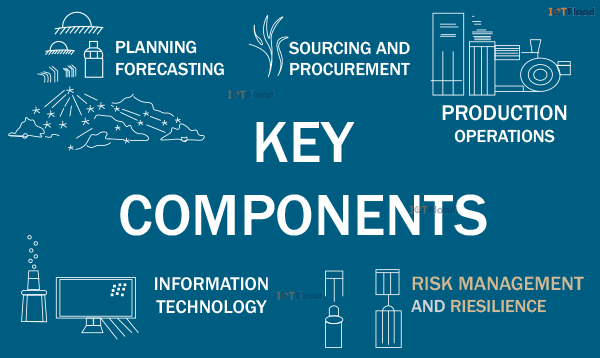
Key Components:
The following are essential elements of supply chain management:
Planning and Forecasting: To satisfy consumer demand while minimizing costs and optimizing resources, this includes demand forecasting, production planning, inventory management, and capacity planning.
Sourcing and Procurement: This entails locating suppliers, negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring that materials and components required for production are acquired on time and within budget.
Production and Operations: This includes scheduling, quality control, and optimizing production efficiency to satisfy demand and uphold product quality standards.
Logistics and distribution: This includes handling shipping, receiving, warehousing, storing inventory, filling orders, and delivering goods to clients in an economical and timely manner.
Information Technology (IT) and Integration: Technology such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, data analytics, and supply chain management software is used to increase visibility, expedite processes, and foster cooperation among supply chain partners.
Risk Management and Resilience: To preserve operations’ continuity and resilience, supply chain disruptions, supplier dependencies, geopolitical issues, natural disasters, and market changes are just a few risks that SCM must recognize and mitigate.
Cooperation, communication, openness, flexibility, and constant development are necessary for effective supply chain management at every level of the process. This will maximize productivity, cut expenses, raise customer happiness, and create a competitive edge.
Working
To facilitate the flow of goods and services from suppliers of raw materials to final consumers, supply chain management, or SCM, integrates several different procedures, actions, and parties. To predict product demand, businesses first forecast and plan it based on past data, consumer preferences, and market trends. Based on these projections, procurement teams source components and raw materials from suppliers, negotiate contracts and guarantee on-time delivery. As soon as materials are obtained, production and operations teams begin working on product manufacture, inventory control, and quality standards maintenance.
Logistics and distribution teams plan transportation, warehousing, and order fulfilment to guarantee that goods reach customers on schedule. Information technology is essential to these operations because it streamlines workflows, gives supply chain participants visibility into the chain, and encourages communication and cooperation. SCM also includes risk management techniques to deal with possible disruptions, such as problems with suppliers, hold-ups in transit, or unforeseen changes in demand.
A company’s ability to react to changing market conditions, cut costs, increase customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge largely depends on its ability to continuously monitor, evaluate, and optimize its processes.
What is IoT in Supply Chain Management?
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolutionises supply chain management (SCM) by facilitating a smooth data flow throughout the ecosystem. To gather real-time data, Internet of Things devices—such as sensors, RFID tags, GPS trackers, and smart meters—are strategically placed at various points across the supply chain.
To ensure maximum production efficiency and minimize downtime, IoT sensors, for example, monitor equipment performance in manufacturing facilities, identify anomalies and provide maintenance warnings. IoT devices in warehouses also track inventory levels, monitor humidity and temperature during storage, and automate inventory management tasks like order fulfilment and stock restocking.
By facilitating prompt decision-making based on precise data, this degree of real-time visibility increases inventory correctness and improves supply chain responsiveness. IoT-enabled cars and containers offer condition monitoring, route optimization, and position tracking for use in logistics and transportation. This enables supply chain managers to monitor shipments as they are traveling, plan the best delivery routes to cut down on expenses and delays, and guarantee the safety and quality of the goods at all times. IoT in SCM uses automation and data-driven insights to improve supply chain network performance, save costs, minimize risks, and increase customer satisfaction.
The Four Implementations of IoT in the Supply Chain
IoT is changing the supply chain landscape, and your four deployments provide a thorough overview. This is an organised synopsis that is predicated on your work:
Manufacturing Products: IoT devices on factory floors facilitate just-in-time manufacturing, boost product development by providing data feedback, improve defect diagnosis, and increase production process transparency.
Products for Shipping: Fleet management and environmental monitoring for temperature-sensitive items are included in IoT-enabled shipping, which offers tracking, visibility, and monitoring of goods from the point of origin to the destination. This leads to better risk minimization, compliance reporting, and logistics management.
Innovative Warehousing: Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in warehouses guarantee ideal storage conditions, automate inventory control, give real-time problem alerts, make tracking via linked devices like RFID easier, and improve overall inventory handling efficiency.
Store Placement and Final Sale: Thanks to the Internet of Things, manufacturers and retailers may provide consumers with transparency about sourcing, production timetables, and other pertinent data points by tracking and reporting items’ journeys from raw materials to the store.
Each of these applications demonstrates how IoT is revolutionising supply chain operations through the use of data-driven insights, automation, and connection throughout the entire supply chain ecosystem.
How does IoT transform SCM?
This is how IoT changes supply chain management:
Real-time Monitoring: Internet of Things (IoT) devices constantly monitor environmental factors, equipment performance, and inventory levels. For instance, warehouse sensors monitor stock levels to guarantee ideal inventory control and minimize cases of stockouts or overstock.
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing consumption trends and performance data, IoT-enabled equipment can forecast maintenance requirements. This proactive strategy lowers maintenance costs, extends the asset’s life, and minimizes downtime.
Supply Chain Visibility: IoT data provides complete supply chain visibility from production to delivery. This visibility improves overall supply chain efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and route optimisation.
Enhanced Traceability: The Internet of Things makes traceability possible by monitoring the location and flow of commodities along the supply chain. This is especially helpful for sectors like food and pharmaceuticals, where law requires traceability to ensure quality and safety.
Data-driven Insights: Actionable insights for improved decision-making are obtained by combining IoT-generated data with analytics and machine learning. For example, route optimization, fuel economy, and delivery time improvements are all made possible by analyzing transportation data.
Through improved visibility and data-driven optimisation, enterprises may use IoT in SCM to optimize operations, lower costs, minimize risks and provide better customer experiences.
Real-Time Visibility: Seeing the Unseen
IoT sensors enable real-time visibility, revolutionizing supply chain management. They eliminate the blind spots and uncertainties prevalent in conventional supply chain operations. IoT sensors integrated into a range of supply chain assets enable businesses to track and monitor their items in transit with previously unheard-of precision and promptness.
Accurate location tracking is a significant advantage, as GPS and other location technologies give precise information on the locations of goods. Supply chain managers can use this information to make well-informed decisions about deliveries, inventory control, and general logistics planning. For instance, they can redirect shipments to prevent delays or optimize delivery routes based on current traffic conditions.
Monitoring the environment is another essential function made possible by IoT sensors. These sensors ensure that goods like medications or perishables are transported and stored in the best possible circumstances by monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental parameters. This aids in preserving the quality and integrity of the product along the supply chain.
Furthermore, proactive problem-solving is made possible by real-time data from IoT devices. Supply chain managers possess the ability to promptly detect potential problems, including equipment breakdowns or delays in transit. With these early detection capabilities, they may minimize delays and maintain uninterrupted operations by quickly taking corrective action, such as rerouting shipments, modifying production schedules, or sending out maintenance teams.
Thanks to the real-time visibility provided by IoT sensors, supply chain stakeholders are empowered with actionable data, better decision-making skills, and more operational agility. This increases productivity, lowers costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
Optimizing Every Step: From Warehouse to Customer
Beyond only improving visibility, supply chain management can benefit greatly from IoT. Utilizing the abundance of information gathered by Internet of Things devices, companies may enhance workflows and boost productivity throughout the whole supply chain:
Warehouse Automation: IoT sensors are essential for guiding robots and automated systems in warehouses. These sensors enable accurate product picking, packing, and transportation by providing real-time data on inventory locations. This automation boosts output, lowers the possibility of human error, and improves warehouse efficiency.
Inventory Optimisation: Real-time data from IoT devices makes optimizing inventory levels possible. By regularly checking stock levels, businesses can prevent stockouts and overstock scenarios, which improves inventory management procedures and lowers carrying costs. IoT data also makes better demand forecasting possible, guaranteeing that the appropriate amount of inventory is available when it is needed.
Route optimisation: Traffic and weather data collected by IoT-enabled devices can be used to establish the best possible delivery routes. By evaluating this data in real-time, businesses may select the most economical routes, use less fuel, shorten delivery times, and improve overall logistics efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors gather useful information about equipment health and performance. Proactive maintenance tasks are made possible by the ability to use this data to anticipate probable equipment faults before they happen. By proactively addressing maintenance concerns, businesses may reduce downtime, increase equipment lifespan, and enhance overall operational reliability.
By using IoT data for predictive maintenance, inventory optimization, route optimization, and warehouse automation, businesses may optimize their supply chains, cut expenses, better utilize their resources, and provide better customer experiences.
How to implement and scale supply chain IoT
The correct tools and a strategic strategy are necessary for the successful implementation and scalability of supply chain IoT solutions. Selecting a trustworthy MQTT messaging engine, such as EMQ X, is essential. With the potential to connect over 50 million devices and manage tens of millions of concurrent clients, this message engine is renowned for its scalability. In a supply chain setting, this scalability is essential for handling the varied and expanding network of IoT devices.
Many of the world’s top businesses choose EMQ X for its scalability in IoT supply chain management. Its capacity to manage massive data volumes and maintain dependable connections guarantees seamless supply chain operations. It is highly advantageous to collaborate with IoT Erlang Solutions specialists to effectively use EMQ X and ensure the success of your IoT supply chain effort. These experts have extensive real-time distributed system development experience using EMQ X and can offer consultancy services for your project at any point, from expansion and optimization to planning and execution.
IoT Erlang Solutions experts provide essential support services like routine health checks, monitoring, and consulting. These services support the system’s dependability, early problem detection, and long-term performance optimisation. With their knowledge, you can maximise your supply chain management investment in EMQ X and IoT.
IoT Applications in Supply Chain Management
IoT applications for supply chain management provide numerous advantages for various operational elements.
Inventory management: Internet of Things sensors automate reordering procedures, monitor stock levels closely, and offer insightful data on demand trends. This improves overall inventory planning efficiency, decreases stockouts, minimizes surplus inventory, and improves inventory accuracy.
Asset Tracking: IoT makes real-time tracking and tracing of assets, including trucks, pallets, and containers, possible. With this visibility, asset deployment and management decisions can be made more effectively, asset security-enhanced, losses and theft avoided, and asset utilization optimized.
Predictive analytics: Supply chain managers may use IoT data and advanced analytics technologies to forecast demand trends, optimize production schedules, identify possible dangers in the supply chain, and make data-driven decisions to increase overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Cold Chain Monitoring: IoT sensors are essential for monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors during the transit and storage of temperature-sensitive goods such as food and medications. This improves product safety and integrity, lowers spoilage, and guarantees adherence to quality standards.
Supplier Collaboration: IoT enables real-time supplier collaboration by exchanging data on demand projections, inventory levels, production schedules, and delivery status. This partnership produces greater business outcomes and consumer satisfaction through improved supplier performance, responsiveness, and overall supply chain agility.
Real-World Examples of IoT in SCM
The following are some actual cases demonstrating how IoT is being used in supply chain management (SCM):
Amazon’s Use of IoT in Warehouses: To improve efficiency, Amazon extensively uses IoT in its warehouses. IoT sensors guide robots for picking and packing, monitor equipment health, measure inventory levels, and optimize warehouse layouts for effective product transportation. This degree of automation and data-driven decision-making improves productivity and order fulfilment accuracy.
Maersk’s Smart Containers: Throughout its global transportation network, Maersk uses Internet of Things-enabled smart containers to monitor cargo conditions. These containers include real-time sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, vibration, and location. This data serves to guarantee the quality and safety of commodities, particularly perishable ones, throughout the supply chain.
Coca-Cola’s vending machines: To collect information on inventory levels, product popularity, and machine performance, Coca-Cola has integrated Internet of Things technology into its vending machines. This data increases operational efficiency and customer happiness by enabling predictive maintenance, restocking schedule optimization, and product offering customisation based on client preferences.
Tesla’s Supply Chain Optimisation: To optimize its supply chain, Tesla uses data analytics and the Internet of Things. IoT sensors optimize production workflows, track the movement of materials and components within manufacturing facilities, and offer real-time visibility into supply chain activity. Because of this, Tesla can meet consumer demand efficiently, maintain low inventory levels, and shorten lead times.
Walmart’s IoT-powered Supply Chain: To manage goods throughout its shops and warehouses, Walmart uses IoT devices, including RFID tags and sensors. Thanks to this real-time visibility, Walmart is able to increase the effectiveness of its supply chain operations overall, optimize stock levels, avoid stockouts, and improve inventory accuracy.
These illustrations show how top businesses in various sectors use IoT technologies to boost innovation, increase operational effectiveness, cut expenses, and provide customers with improved supply chain management experiences.
Benefits of IoT in SCM
The Internet of Things, or IoT, revolutionizes traditional operations and boosts competitiveness, efficiency, and agility in supply chain management (SCM). Among the main advantages of IoT in SCM are:
Real-Time Visibility: From procuring raw materials to delivering final goods to customers, IoT offers real-time visibility across the whole supply chain. Thanks to this visibility, supply chain managers can monitor equipment performance, monitor inventory levels, and streamline logistical procedures, which improves decision-making and responsiveness.
Improved Inventory Management: When a stock hits specific criteria, automatic reordering is initiated using IoT sensors that track inventory levels in real time. This optimizes inventory management procedures and lowers carrying costs by lowering stockouts, minimizing surplus inventory, and improving inventory accuracy.
Enhanced Traceability and Transparency: Thanks to the Internet of Things, goods can be tracked and traced along the whole supply chain, increasing transparency and traceability. This is especially important for sectors like food and pharmaceuticals subject to strict regulations, as IoT helps guarantee quality control, safety standards, and compliance.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors collect data on equipment performance and health, enabling predictive maintenance. By anticipating possible equipment faults before they happen, businesses may decrease equipment downtime, increase operational dependability, and prolong equipment lifespan.
Optimised Logistics and Route Planning: Information from the Internet of Things, such as traffic and weather data, is used to improve logistics and plan routes. As a result, delivery times are shortened, transportation expenses are decreased, and overall logistics effectiveness is raised.
Enhanced consumer Experience: By providing real-time information on order status, shipping updates, and product availability, IoT provides responsive and personalized consumer experiences, enhancing client retention, loyalty, and satisfaction.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Benefits: IoT in SCM generally results in cost savings and efficiency benefits throughout the supply chain by streamlining procedures, cutting waste, optimizing resource usage, and enhancing overall operational performance.
These advantages demonstrate how the Internet of Things is revolutionizing supply chain management and assisting companies in improving their competitiveness, adapting to shifting market conditions and satisfying the demands of stakeholders and customers.
Challenges and Considerations
IoT implementation in supply chain management presents several issues and concerns that businesses must deal with:
Data Security: The interconnectedness of IoT devices increases the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Protecting critical supply chain data and upholding customer trust requires implementing strong data security measures, encryption techniques, access limits, and frequent security audits.
Interoperability: Different vendors’ IoT platforms and devices might be difficult to integrate because of their differing communication protocols, standards, and protocols. Enabling smooth data interchange and collaboration throughout the supply chain network requires establishing interoperability standards, utilizing middleware technologies, and implementing API-based interfaces.
Scalability: Reliable connectivity options, scalable infrastructure, and effective data management techniques are all necessary to scale IoT systems to support a large number of devices and data streams. To accommodate future development and expansion, organizations must invest in scalable technologies and plan for scalability from the beginning.
Costs: Although investing in IoT can lead to long-term advantages, including enhanced decision-making, cost savings, and operational efficiency, there are up-front expenses related to the purchase, installation, upkeep, and training of devices. Businesses must conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, assess the possibility of a return on investment, and rank investments according to their strategic goals and financial limitations.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to industry standards, privacy laws, and data protection requirements is essential when integrating IoT in supply chain management. Organizations must ensure that IoT implementations follow data governance rules, ethical standards, and regulatory requirements to prevent legal and compliance problems.
By proactively tackling these issues and concerns, organizations may optimize the advantages of IoT in supply chain management while reducing risks and guaranteeing a safe, effective, and scalable IoT infrastructure.
How can IoT Improve Supply Chain Sustainability?
Better visibility, resource optimisation, and proactive control of environmental impacts are just a few ways the Internet of Things (IoT) may boost supply chain sustainability. IoT can improve supply chain sustainability in several ways, including these:
Real-time Monitoring: Throughout the supply chain, IoT sensors can track waste production, emissions, water use, and energy use in real time. To lessen environmental effects, this data assists in identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
Effective Resource Management: IoT streamlines manufacturing procedures, equipment utilization, and transportation routes, making it possible to use resources like electricity, water, and raw materials more effectively. Smart sensors, for instance, can modify energy consumption according to demand to save energy and lessen carbon emissions.
Transportation Optimisation: IoT-powered logistics and fleet management solutions can improve transportation routes, reduce idle time, cut fuel consumption, and lower pollutants. This lowers expenses while improving sustainability by decreasing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Supply Chain Transparency: The Internet of Things (IoT) makes the supply chain transparent by enabling businesses to track the source of raw materials, confirm ethical sourcing methods, and guarantee adherence to environmental laws and norms. This transparency encourages ethical sourcing and production methods while fostering confidence among stakeholders and customers.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors can monitor equipment performance and identify potential maintenance concerns before costly breakdowns occur. By taking a proactive stance, downtime is decreased, equipment longevity is increased, and resource waste from unnecessary maintenance is reduced.
Waste Reduction: IoT makes waste management easier by monitoring waste production, implementing recycling and waste reduction plans, and streamlining waste disposal. Overall, IoT enhances supply chain sustainability by lowering the amount of waste dumped in landfills and encouraging circular economy methods.
Data-driven decision-making: IoT data analytics offer helpful information for making well-informed choices on sustainability-related projects. Businesses can recognise patterns, establish goals, track advancement, and constantly enhance sustainable processes throughout the supply chain.
IoT enables businesses to embrace a comprehensive strategy for supply chain sustainability by incorporating environmental factors into routine business operations, maximizing resource utilization, cutting waste, and promoting continuous development towards sustainable practices.
Some Potential Cost-saving Benefits
IoT implementation in supply chain sustainability can save money by streamlining processes, cutting waste, increasing productivity, and lessening environmental effects. The following are some possible cost-saving advantages of IoT adoption in supply chain sustainability:
Improved Inventory Management: IoT sensors give businesses real-time access to inventory data, allowing them to minimize stockouts, reduce surplus inventory, and optimize stock levels. This results in cost savings by lowering carrying costs, requiring less storage space, and increasing inventory turnover rates.
Improved Asset Utilization: The Internet of Things makes it possible to track and use assets like machines, cars, and equipment more effectively. Optimizing asset usage can save businesses money by extending the life of their assets, cutting down on idle time, and improving operational efficiency.
Energy Efficiency: Smart energy management systems and Internet of Things sensors assist in tracking and regulating energy usage in buildings and warehouses. By optimizing energy usage based on demand patterns and real-time data, firms can attain energy savings and minimize energy expenses over time.
Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance enabled by IoT technology helps anticipate maintenance requirements and identify equipment problems early. This proactive strategy decreases maintenance and repair costs, minimizes production disruptions, and reduces unscheduled downtime.
Optimized Logistics: IoT-powered fleet management and logistics solutions optimize transportation routes, decrease fuel consumption, and increase vehicle efficiency. Lower fuel costs, fewer maintenance charges, and more overall logistical efficiency all result in cost savings.
Streamlined Processes: IoT simplifies supply chain operations by automating tedious jobs, increasing workflow effectiveness, and lowering manual errors. Lower labor costs, increased productivity, and improved process accuracy lead to savings in operating costs.
Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility: The Internet of Things (IoT) gives businesses real-time visibility into supply chain operations, enabling them to track shipments, monitor delivery status, and spot possible bottlenecks or delays. This visibility decreases lead times, boosts supply chain efficiency, and minimizes the cost of expedited shipments or rush orders.
Integrating IoT into supply chain sustainability can result in large cost reductions in several operational areas, such as supply chain visibility, maintenance, asset utilization, inventory management, and energy efficiency. When companies integrate IoT into their supply chain plans, these cost-saving advantages boost profitability, resource efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Future Outlook
IoT in supply chain optimization has a bright future thanks to technological breakthroughs that are changing the face of operations and logistics. The broad deployment of 5G connectivity is one significant advancement. 5G networks will facilitate smooth connection between IoT devices with their high-speed, low-latency capabilities, enabling quicker data transmission and real-time monitoring. This enables supply chain managers to make quicker and more responsive decisions by providing them with real-time information on inventory levels, equipment status, and shipping status.
Another important development is the increasing use of edge computing in supply chain management. Edge computing processes data at the network’s edge, closer to the source, as opposed to depending only on centralized cloud servers. IoT devices can reduce latency and reliance on internet access by executing commands locally and performing data analytics through edge computing technology. This increases the overall efficiency of the supply chain by enabling quicker response times for automated procedures like inventory replenishment orders or predictive maintenance alerts.
Additionally, as AI-driven analytics advance, businesses can extract valuable insights from massive data from the Internet of Things devices. In addition to analyzing past data and spotting trends, machine learning algorithms can automate decision-making processes, improve routing algorithms, forecast demand variations, and more. Supply chain experts are better equipped to allocate resources optimally, make educated judgements, and proactively handle possible interruptions before they harm operations with this level of intelligence.
The future of supply chain optimization with IoT is defined by hyperconnectivity, real-time data processing, and autonomous decision-making as these technologies converge and develop. Businesses that take advantage of these developments and smoothly incorporate IoT into their supply chain operations will have a competitive advantage because they will increase customer happiness, cut costs, improve operational efficiency, and spur innovation in a changing market. IoT-powered intelligent supply chain technology is about to enter its next phase, offering enterprises in various industries a new level of adaptability, resilience, and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Supply chain management has undergone a paradigm change with the incorporation of IoT, which has transformed traditional supply chains into flexible and dynamic ecosystems. By utilizing IoT solutions, organizations can quickly adapt to shifting consumer expectations, market trends, and supply chain disruptions. By maximizing resource use and reducing waste, this agility raises customer happiness, lowers operational risks, and promotes sustainable growth.
Supply chain optimization has a bright future as businesses embrace IoT more fully. With more automation through IoT-enabled devices and autonomous systems, processes will be streamlined, efficiency will increase, and operating costs will be reduced. Moreover, IoT’s predictive capabilities will make proactive decision-making, preventive maintenance, and optimized inventory management possible, boosting competitiveness in the market and raising service standards.
Collaboration is another critical component of the future IoT-powered supply chain landscape. IoT platforms and linked systems will make supply chain partners’ seamless integration and data exchange possible, resulting in greater openness, confidence, and cooperation. In addition to improving supply chain performance, this cooperative strategy will promote value-driven alliances, innovation, and co-creation—all of which are essential for success in the digital age.