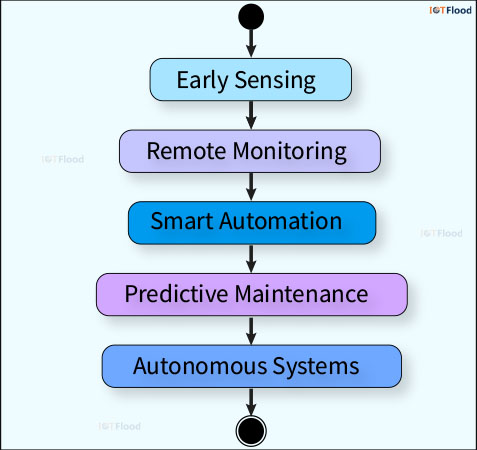
Evolution of Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a new paradigm transforming traditional lifestyles into technologically advanced ones. Technology has advanced from large desktop computers to small, portable mobile gadgets. It is now making another appearance, incorporating intelligence into everyday items. These changes brought about by IoT include smart cities, smart homes, pollution reduction, energy conservation, smart transportation, and smart industries.
The Internet of Things, IoT, has taken off over the years. IoT has become this huge, transforming thing with so many everyday objects now connected to the internet and industries changing.
In this article, I’m gonna take us through the whole story of IoT – from where it started to where we’re at now.
What is IoT?
Imagine a city where every aspect of your life is connected. In a city where street lights brighten or dim based on the actual need, garbage bins send signals when full, and buses adjust routes in real-time. This isn’t merely a futuristic fantasy but an authentic worldwide utilization of the Internet of Things (IoT). The Internet of Things (IoT) transforms urban landscapes into efficient and responsive environments in cities like Barcelona.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data via the Internet. These gadgets vary from everyday items such as smartphones and smart home appliances to industrial sensors and self-driving vehicles.
Emergence and Early History
1982: One of the early IoT devices was created when a graduate student at Carnegie Mellon University connected a vending machine to ARPANET, a significant turning point in the history of the Internet.
1989: Tim Berners Lee introduced the World Wide Web framework, which laid the groundwork for worldwide connectivity.
1990: John Romkey of MIT designed a toaster that could be operated via the internet, regarded as the world’s first IoT gadget.
1999: Kevin Ashton invented the term “Internet of Things,” imagining a future where everyday objects would be connected and communicate seamlessly.
Evolution of IoT
IoT has come a long way from the concept of connected devices to its widespread use in all facets of our lives. IoT was created to enable M2M communication and automation in the industrial environment, but it has quickly grown to span a wide range of domains. Thanks to wireless technology, sensor miniaturization, and data analytics, IoT has grown beyond its early boundaries and now covers industries such as healthcare, agriculture, transport, and intelligent cities.
Innovations and advances in technology have caused the Internet of Things to change dramatically over time:
Technological advancements: The creation of low-power communication protocols, the shrinking of CPUs, and the accessibility of inexpensive wireless connectivity have made the Internet of Things (IoT) more widely used.
Sensor Technology: Developing effective sensors allowed for data collection on various characteristics such as temperature, humidity, and motion, driving a wide range of IoT applications.
Exponential Growth: The Internet of Things has experienced exponential growth in various sectors, including industrial automation, smart homes, healthcare, and agriculture.
Impact of COVID-19 on IoT
The COVID-19 epidemic has dramatically accelerated the implementation of IoT technology in various areas, including IT, education, finance, and healthcare. IoT devices are being used in healthcare facilities to monitor patients remotely via networked devices and to stop the virus’s spread effectively. These gadgets, for instance, evaluate important patient metrics and instantly inform healthcare professionals. Reducing the effects of COVID-19 has been made possible in large part by the application of IoT technology. Furthermore, IoT systems help organizations resume normal operations by aiding in the development and implementation of contact-tracing applications.
Technologies Facilitating the Growth of IoT
Venturing into the realm of Internet of Things (IoT) growth is a thrilling journey. A wide range of technologies from several areas support the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT).
Following are some key technologies that are contributing to the expansion of IoT:
1. Wireless Connectivity Protocols: Data transmission in Internet of Things devices relies heavily on wireless connection. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, LoRaWAN, and NB-IoT are protocols that offer connectivity choices appropriate for various IoT use cases.
2. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI): These two fields of study allow Internet of Things (IoT) devices to analyze data locally or in the cloud, extracting useful insights, spotting discrepancies, and deriving independent conclusions. This is necessary for applications such as predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and intelligent automation.
3. Blockchain: Blockchain guarantees safe and transparent data transfers and transactional activities in IoT ecosystems. It improves data integrity, simplifies device identity management, and allows for secure micropayments and smart contracts, critical for trustworthy IoT deployments, particularly in supply chain management and healthcare.
4. Sensor Technologies: Gathering information from the real world, sensors form the core of the Internet of Things. Miniaturization, increased precision, and reduced power consumption are some of the advancements in sensor technology that allow a broad spectrum of Internet of Things (IoT) devices to be deployed in various industries, ranging from healthcare to environmental monitoring.
5. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): IoT integration of AR and VR technologies is growing, offering more immersive experiences and improved human-machine interaction. They add interactive interfaces and visualizations to IoT solutions, making them useful for consumer experiences, training simulations, and remote maintenance.
Delving into the Benefits of IoT
In a world where every device whispers secrets to the digital universe, the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges as the wizard, conducting a symphony of interconnected brilliance. IoT presents a world where the ordinary becomes extraordinary, and the mundane becomes magnificent, from enhancing productivity to transforming comfort.
Let’s now examine the variety of advantages this technological wonder has to offer:
1. Innovation and New Business Models: IoT promotes innovation and allows for the creation of new business models. IoT technologies, for instance, encourage the development of new mobility services, such as ride-sharing and car-sharing platforms and self-driving cars in the automobile industry.
2. Improved Data Collection and Analysis: Internet of Things devices generate tremendous amounts of data that can be examined to extract important information. This information can enhance decision-making procedures, streamline operations, and spot unexplored market segments.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life: The Internet of Things (IoT) improves our quality of life by invisibly incorporating technology into our surroundings, whether smart homes, wearable technology, or connected cars. IoT improves safety, well-being, and convenience—managing home appliances from smartphones to tracking health parameters in real-time—thereby raising our standard of living.
4. Facilitating Innovation: The Internet of Things (IoT) acts as a stimulant for innovation, generating new goods, services, and business strategies. The possibilities are limitless, from smart grids revolutionizing energy distribution to connected healthcare devices altering patient care, cultivating a culture of constant growth and technical advancement.
5. Sustainable Solutions: IoT supports sustainability initiatives in several industries by reducing waste, maximizing resource utilization, and enabling predictive maintenance. IoT plays a critical role in creating a future that is more secure and sustainable, whether it is through smart cities lowering carbon emissions or smart agriculture saving energy and water.
Current State and Future Prospects
Today, IoT plays an important role in improving efficiency, connectivity, and decision-making across various industries. Smart homes, connected cars, and smart cities are just a few examples of how the Internet of Things transforms our environment.
IoT has enormous potential for future innovation and connectivity as we look to the future. With advances in 5G networks, edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and enhanced security measures, the possibilities for IoT applications are infinite.
The transition from analog to smart gadgets demonstrates how a simple idea may become a technological revolution that shapes our modern environment. As we continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the Internet of Things will definitely play a critical role in building a more interconnected and intelligent future for all.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things has undergone an incredible journey of invention, collaboration, and adaptability throughout history. IoT has evolved from its humble beginnings as a concept to its widespread presence in practically every part of modern life, thanks to technological advances, communication protocols, and data analytics.
As we look back on its history, we see the merging of differing disciplines, from telecommunications to artificial intelligence, to form a seamless network of interconnected gadgets. Yet, there is far more to this growth. Each day, IoT expands its capabilities and reshapes industries, society, and economies worldwide.
Let us learn from the past, seize the opportunities, and approach the rapidly evolving IoT environment with curiosity, creativity, and foresight as we stand on the edge of a future filled with promise and opportunity. The key to opening up a world of limitless possibilities, where connectedness defies boundaries and revolutionizes how we work, live, and interact with the world around us, rests in this evolutionary path.